With the quickly growing popularity of blockchain and cryptocurrencies, we cannot help but start exploring this new world that nobody heard of even a decade ago. We may ignore it for a while, however, it looks like crypto-money has come to stay, and it may very well start laying down its own rules, and quite soon. Even Bill Gates admitted that “Digital currency is the future of money.”
Well, since our lives are anyway dependent on money and the way we handle it, it may be a wise move to get a better look at what the crypto space has in store for us.
One of the blockchain-based concepts that has sprung in the recent years is the concept of ICO. Since its appearance, it has grown immensely popular and now attracts both startups and investors. The ICO Calendar on Cointelegraph lists about three dozen ongoing ICOs and approximately the same number of upcoming ones. As ICOs seem to have become an essential part of the global fundraising structure, we have decided to publish a series of articles explaining the very essence of an initial coin offering and giving answers to the most frequently asked questions.
So, welcome to Part 1 of our series where you will learn what ICO is and how it works. To begin with, take a look at the infographic and scroll down to see the detailed description.
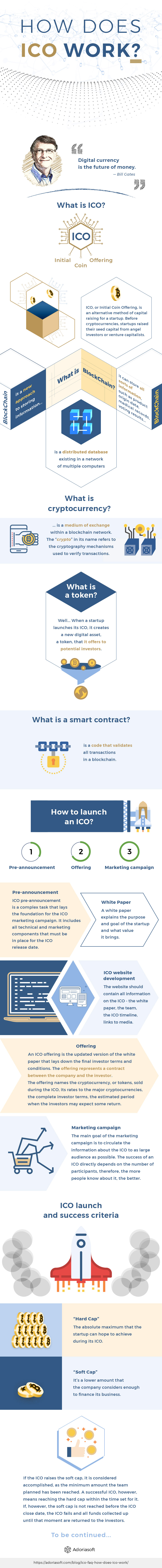
What is ICO?
ICO, or Initial Coin Offering, is an alternative method of capital raising for a startup. Before cryptocurrencies, startups raised their seed capital from angel investors or venture capitalists. Now, ICOs offer a much faster, decentralized and less bureaucratic way of collecting the amount that the startup needs.
During an ICO, investors purchase new crypto-coins, called tokens, paying with the globally accepted cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin or Ether. This is how the startup capital is raised.
Before we go on into the workings of initial coin offering, let’s look into the basic ICO terminology and the concepts behind it. We are going to use these terms quite often in our research of the ICO structure and functioning, so it’s better to be clear on their meaning.
What is blockchain?
Let’s start “ab ovo” and look at the technology that is at the foundation of everything related to cryptocurrencies and ICOs.
A blockchain technology is a new approach to storing information. Simply put, it is a distributed database existing in a network of multiple computers. The information is shared between all nodes in the system and is updated in a synchronous manner. There is no central information storage in a blockchain which makes it extremely difficult to hack into. Also, blockchain prevents any user from modifying any existing record, thus creating unprecedented verification and validation opportunities.
Most often, the blockchain technology supports cryptocurrency transactions. However, it can store all sorts of information, such as product origin data, medical records, voting results, etc. Blockchain provides a perfect environment for non-bureaucratic, secure, transparent peer-to-peer transactions that are also in some cases more cost-effective than traditional financial operations. Since blockchain supports no central database and allows direct transactions between members, the maintenance costs are at the absolute minimum.
There are large and small blockchains created for different purposes and groups of users. In all cases, their operation principle is the same, and their effectiveness depends on the quality of their development. There are many details in blockchain creation. And all of them are equally important. A properly functioning blockchain is usually the work of professionals that know all ins and outs of the technology. Moreover, they can be relied upon to deliver a good product. We came to this conclusion from our blockchain development experience that we acquired in a number of successful projects.
What is cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a medium of exchange within a blockchain network. The “crypto” in its name refers to the cryptography mechanisms used to verify transactions.
Basically, each cryptocurrency is a record in a database that can be modified only when certain conditions are fulfilled. Transactions are verified by all participants in the blockchain network – a distributed ledger where each transaction can be traced through all its stages.
Thus, cryptocurrencies form a totally new approach to financial transactions, by delivering a secure and verified method of exchange.
What is a token?
A token is a concept that mostly refers to ICOs. When a startup launches its ICO, it creates a new digital asset, a token, that it offers to potential investors. The capital raising process is done through the token sale that is announced together with the ICO.
During the token sale, investors purchase the tokens with other cryptocurrencies that are already commonly circulating, usually Bitcoin or Ether. The startup capital will consist of Bitcoin or Ether while the investors become token holders.
During the ICO, the startup may issue tokens of two major types:
-
- Security tokens that can be traded at cryptocurrency exchanges and bring profit to investors. When the project becomes successful, the value of tokens, or the new cryptocurrency, raises, and this is what investors expect.
- Utility tokens that provide access to the product or service that the startup plans to develop. By investing in utility tokens, users can support the project and then benefit from the increasing demand for the company’s product.
What is a smart contract?
A smart contract is another blockchain entity that has a direct relation to ICOs. The advantage of blockchain is in its decentralized structure. The transactions are not verified or approved by any “middlemen” there. Low maintenance cost is, among others, is due to this absence of middlemen.
However, there must be a mechanism for monitoring and validating cryptocurrency transactions and other blockchain-based transactions. For that purpose, companies use smart contracts.
In a nutshell, a smart contract is a code that validates all transactions in a blockchain. For each transaction, a smart contract stores the conditions that must be fulfilled by both parties and the date when the transaction is to be executed.
Smart contracts are self-executing, which means that no human intervention is required. On the date of the transaction, it checks that, for example, one party has provided the goods and the other party has made the payment. If both conditions are fulfilled, the smart contract releases the goods to the buyer and the money to the seller. If any party has failed, the smart contract returns the money or the goods to their owners and the transaction is canceled.
Each ICO includes a smart contract to regulate the token transactions. This way, the investors’ interests are safe.
How to launch an ICO?
Now that we are familiar with the crypto terminology let’s look at ICOs and how to launch one. We will describe the major tasks that the ICO development team faces and the way they can be accomplished. Recently, we have participated in an ICO development project for Digitex Futures, a cryptocurrency exchange, and we can use it as an example of a wisely prepared ICO.
Each ICO begins with a preparatory stage that is the most important, as it determines the success of the initial coin offering. Generally, the ICO preparations consist of three components that may overlap in time:
-
- Pre-announcement
-
- Offering
- Marketing campaign
Pre-announcement
ICO pre-announcement is a complex task that lays the foundation for the ICO marketing campaign. It includes all technical and marketing components that must be in place for the ICO release date.
White Paper
You will find a white paper in every ICO. In fact, you will find a white paper in every capital-raising campaign, both crypto and fiat. A white paper explains the purpose and goal of the startup and what value it brings.
A typical white paper states the problem and describes the solution for it. A white paper issued for an ICO describes the startup for which the capital is to be raised. Potential investors should be able to judge the value and the soundness of the solution from the white paper. In short, a white paper should convince the investors to invest.
Of course, a white paper is not a purely marketing or promotional document. On the contrary, a white paper should represent a research that forms the basis of the project. Having read the white paper, the visitor should learn how they are going to benefit from investing. And here we mean figures, calculations, diagrams, and statistics.
For Digitex Futures, the white paper explained the advantages of commission-free cryptocurrency trading and described the trading methodology that the startup was going to implement. It also included the token and profit distribution calculations, so that potential investors could estimate their earnings.
At the pre-announcement stage, the company circulates its white paper in the industry-specific media to gauge the investor interest towards the startup.
ICO website development
All ICO-related activity occurs on its dedicated website. The website should contain all information on the ICO – the white paper, the team, the ICO timeline, links to media. On the other hand, it should provide the opportunity for the visitors to register as investors – the investor cabinet where each participant can set up their cryptocurrency wallet.
Another important thing is the implementation of proper security mechanisms to ensure ICO data protection from cyber attacks.
Offering
An ICO offering is the updated version of the white paper that lays down the final investor terms and conditions. The offering represents a contract between the company and the investor.
The offering names the cryptocurrency, or tokens, sold during the ICO, its rates to the major cryptocurrencies, the complete investor terms, the estimated period when the investors may expect some return.
Usually, together with the ICO offering, the company announces its date and starts the countdown timer on the ICO website.
Marketing campaign
A marketing campaign for an ICO starts with the first issue of the white paper. However, it reaches its peak after the offering publication. This point is in most cases about one month before the actual ICO, and this month is tightly packed with marketing activities.
The main goal of the marketing campaign is to circulate the information about the ICO to as large audience as possible. The success of an ICO directly depends on the number of participants, therefore, the more people know about it, the better.
During the marketing campaign, the startup uses all possible channels to reach its potential investors. Usually, the campaign includes creation of a dedicated Facebook and Twitter accounts especially for the ICO purposes. They usually publish the latest ICO news and developments.
A good idea is to prepare several articles about the company, the project it is planning to implement, the solution it is trying to resolve and about the upcoming ICO. Many startups use Medium to publish their ICO-related articles, as Medium is the resource that technology-focused people tend to frequent.
As part of an ICO marketing campaign, startups also open a channel in a messenger service. Via this channel, the startup answers the questions people might have in connection with the ICO. Since ICOs usually aim to attract investors from all parts of the globe, such channel should be monitored 24/7. This way, visitors from all time zones can get answers to their question promptly.
The marketing campaign continues until the ICO launch date.
ICO launch and success criteria
On the ICO date, the token sale opens, and the investors start purchasing tokens with their cryptocurrencies. Most ICOs limit the amount they aim to raise. In fact, they set two limits. One is the so-called “hard cap” – the absolute maximum that the startup can hope to achieve during its ICO. When the proceeds from the token sale reach the hard cap, the ICO closes.
The “soft cap”, on the other hand, is a lower amount that the company considers enough to finance its business. When the token sale reaches the soft cap, it continues until the amount reaches the hard cap or until its close date.
If the ICO raises the soft cap, it is considered accomplished, as the minimum amount the team planned has been reached. A successful ICO, however, means reaching the hard cap within the time set for it. If, however, the soft cap is not reached before the ICO close date, the ICO fails and all funds collected up until that moment are returned to the investors.
Of course, the soft cap and hard cap amounts should be based on the explicit calculations that can be found in the white paper. By studying the white paper, prospective investors also pay attention to the amounts the company aims for and judge whether they are realistic or not.
To be continued
We hope we managed to give you an idea of how ICOs work and what it takes to launch one. In the next articles, we will dive deeper into the specifics of ICO, describe the technical aspects of ICO launch and the components that the company should plan to create ICO. We will talk about the advantages of ICOs for startups and investors and other aspects of this fundraising methodology.
In the meantime, visit our website for the information on our ICO development service and stay tuned for more news from the crypto space.